The SoftSummit 2022 conference brought together industry leaders in software monetization to discuss their insights and experiences within this evolving landscape. With a global audience and leaders in the space sharing their findings, the event was a day packed full of actionable insights, engaging strategies, and detailed use data.
Across the event, three speakers discussed the movement to consumption software monetization billing, tracing the development of this model and the path businesses are taking as they shift towards it.
Although representing three different roles in the industry, a web of insightful connections arose across the presentations given by IDC’s Mark Thomason (Research Director, Digital Business Models and Monetization), and Revenera’s Eric Jensen (Solution Architect) and Scott Niemann (Director, Product Management). As we explore what they touched upon in their sessions, their combined efforts help to construct a picture of how the software industry is developing its monetization strategies, the primary considerations companies must take before adopting, and the best practices to inform this shift.
Let’s move through the presentations by each speaker, highlighting the core information they brought to the conference and outlining how it fits into the developing dialogue around software monetization in 2022.
How is the Software Industry Developing Its Monetization Strategies?
Tracing the development of software industry trends and monetization strategies over the past few years, Mark Thomason began his presentation by breaking down the core differences between software development priorities across two groups. These parties, digital natives and traditional enterprises, are both developing software, but for different reasons and with distinct priorities.
Digital natives (companies that are founded to deliver a digital product) perceive the software they develop as a potential asset for generating a new revenue stream. Alongside profit, they see creating and launching products and platforms as an effective method of gaining a reputation within the community through contributing to open source products.
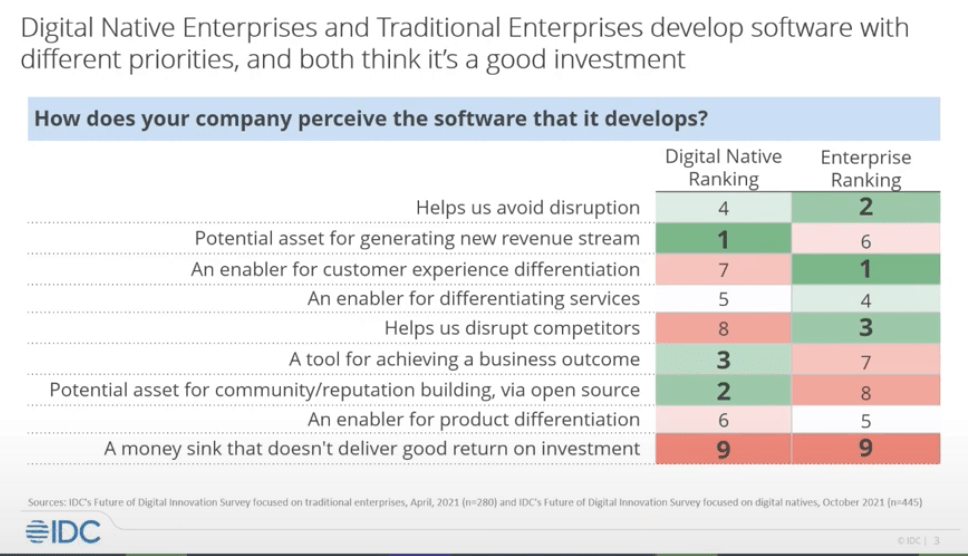
Digital natives are looking to create lasting architecture and to host their own industry marketplaces or sell their software through partners. Among the cloud marketplaces that digital natives are using to sell or buy software, three platforms have risen to the top:
- AVS Marketplace
- Azure Marketplace
- Google Cloud Marketplace
An alternative to moving to a cloud marketplace is creating your own bespoke marketplace, with new ecosystem orchestration platforms providing the infrastructure to create rapid and interconnected subscription-based platforms. Within the world of software monetization, a company hosting its own marketplace is becoming much more common, primarily due to the lowering difficulty bar and cost of entry.
What Monetization Models Follow This Movement to the Cloud or Bespoke Marketplaces?
As deployment models shift toward the cloud, software monetization models are also changing. The most significant change over recent years has been the movement from a perpetual monetization model, where a company buys a license for unlimited use of a product, into a subscription service where businesses are billed at regular intervals.
This change reflects the industry’s desire for recurring revenue and flexibility about how they package and price their software. While perpetual licensing was once the most common model, subscription services are now seen everywhere, from Apple to large-scale B2B companies.
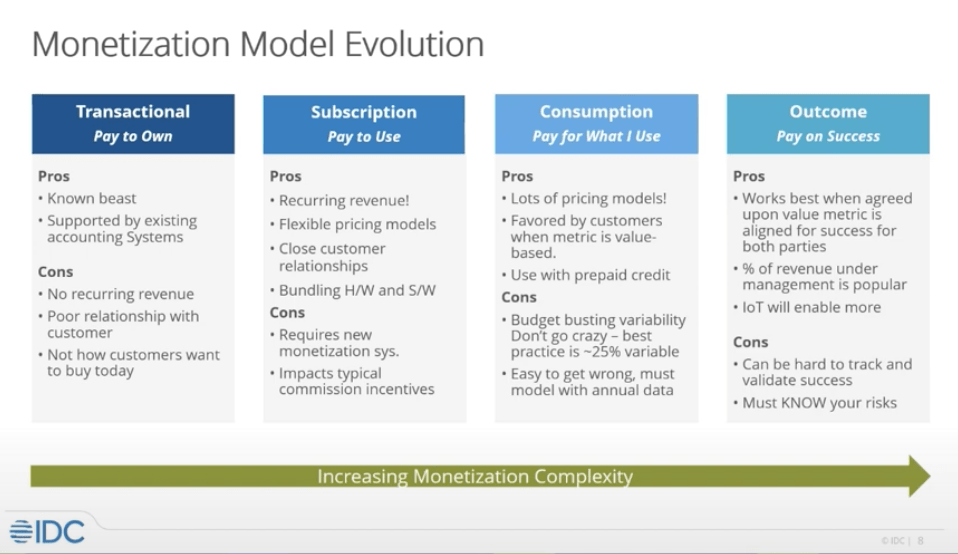
Yet, a further form of software monetization is slowly starting to permeate into the industry, with consumption models favoring businesses that offer complex suites of different possible products or platforms. A consumption model allows clients to buy pre-paid credits, paying directly for what they use over any given time period.
Typically, consumption models are favored as clients can start with a low cost and increase the amount they buy each month with their needs. As a client becomes more familiar and confident with the software, they can integrate it into more processes and directly scale their usage. This system allows the client to directly perceive the value in the software they use, with the clear relation between usage and value benefitting the customer’s needs.
Consumption Software Monetization Is Growing At a Rapid Rate
The software industry is rapidly moving to subscription-based monetization over both deployment models, with this trend increasing at 17.9% CAGR. Comparing this with the segment movement of license and maintenance, which is decreasing at 8.1% CAGR, it’s clear that more flexible monetization models are quickly becoming the industry standard.
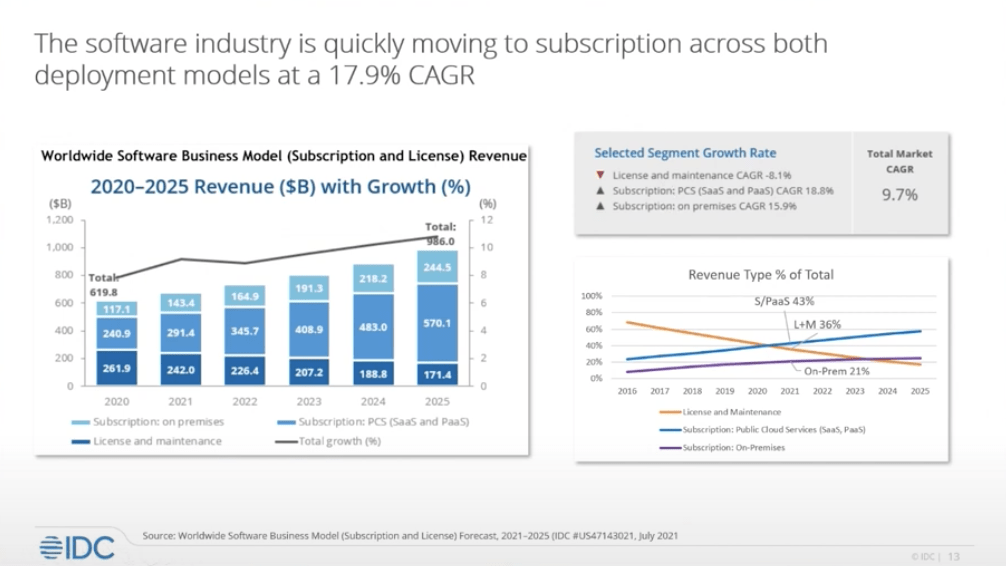
Alongside this industry-wide shift, Mark outlined the best practices which have emerged as this monetization movement has occurred. For a business that is attempting to shift to a consumption model, he suggests that they:
- Limit Risk for New Customers – Place guardrails to ensure customers don’t exceed their desired spending.
- Alter Sales Compensation Models – Sales commissions must have a long tail format to ensure benefits to the sales team remain rewarding.
- Ensure High-Performance Revenue Recognition and Billing – Billing and revenue recognition needs to be time-efficient, meaning that companies must recognize their usage revenue.
- Understand Your Business Usage Model – Unlike a monthly subscription monetization model, consumption is difficult to forecast, meaning that businesses must understand their usage.
Mark concluded his presentation by outlining a roadmap for businesses looking to align themselves with the movement of software monetization into a consumption model. He signaled three core steps of this process:
- Shift to a subscription business model, allowing your business to create recurring revenue, boost valuation, and acquire new customers with less cost.
- Move to a hybrid model, adding cloud features and creating opportunities for expansion.
- Finally, create a SaaS version of the product, allowing for scalable deployment, usage across different tenants, and full API integration for the customer.
With this movement, your business is in a prime position to collect data insights from your customers, helping to calculate churn, create a solid valuation for the price paid, and identify leakage across the product.
What Considerations Should My Company Make Before Adopting a Consumption Model?
Expanding upon Mark’s presentation, Revenera’s Eric Jensen explored the primary considerations that a company should explore before adopting a consumption model of software monetization.
He outlined that there are three main factors that drive companies towards the consumption model:
- Business Maturity – As a consumption model relies on a complete understanding of how clients use your products and which aspects are most commonly utilized, the vast majority of companies that move towards a consumption model are mature companies that have a deep level of self-understanding about usage data.
- Virtualization – As companies move to the cloud, a certain cost is incurred for usage. If a customer is putting a strain on this service, you will need to pass that cost incrementally along the chain.
- Deriving Value – A consumption model directly represents the value that a customer derives against the cost they pay. With this, clients can be more specific about budgeting, using software services to the extent that they perceive the most value from.
Upon meeting one, or several of these conditions, a company will have the motive to move to a consumption monetization model. However, they must fulfill additional requirements of this monetization model.
While motivation may exist, if a company doesn’t understand exactly how their product is consumed, then they clearly are not ready to move to a consumption model yet. Equally, their platform must have incremental costs rather than value accrued over time. An example of this already exists in the world of medicine, where an itemized bill will include non-reusable products that were used or consumed during a trip to the hospital.
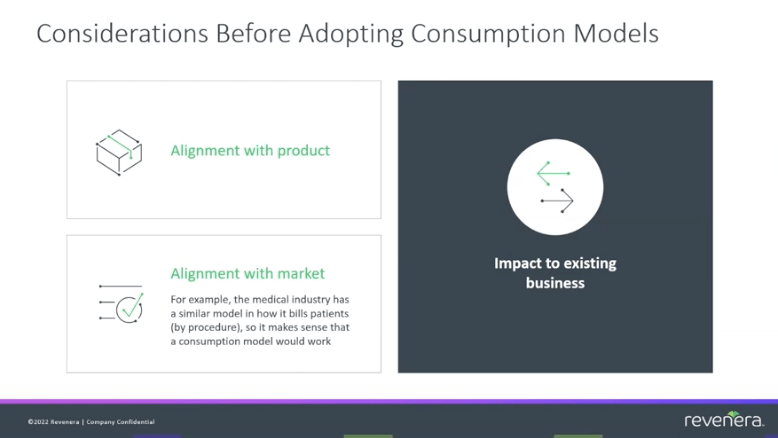
Without a clearly defined alignment with a cost per procedure or action, consumption models can become increasingly difficult to manage as they exist within a pricing gray area. This could lead to disputes with the customer, where they disagree whether a cost incurred is aligned to the specific action taken.
When considering moving to a consumption model, the easiest pathway is where your software has small and repetitive measures that you can bill against.
What Are The Pros and Cons of a Consumption Software Monetization Model?
Once you meet the requirements for implementing a consumption model, there are a range of benefits to this approach that make it an attractive development. Eric outlined three main benefits that are pulling software businesses in this direction:
- Customers Directly See Value – Instead of simply incurring a cost for the right to use software, as in subscription-based billing, customers are billed directly on what they use. This gives a sense of control to the customer as they only pay for the value that they are actively creating in the application.
- Reduces Purchase Timeline – The cost from the outset is only as high as a customer wants to go, with the direct correlation between usage and billing creating a lower bar to entry. However, this can rapidly increase the onboarding timeline as customers feel less stake in beginning to use a company’s software.
- Further Feedback Created For Product Management – The product management team can see directly what customers are spending on and what they’re willing to spend on, helping to outline the most successful or useful parts of a platform.
Of course, with an accumulation of these benefits, the challenges of this monetization strategy also begin to arise. Without a proper understanding of a product’s usage, forecasting billing and revenue is much more difficult with consumption. Equally, if a company’s sales team works on commission, then the movement to a loyalty-dependent system rather than a number of sales will create some disruption.
However, a business can mostly neutralize these drawbacks by fulfilling more of the initial conditions and considerations for adoption. If effective planning is executed ahead of time, your company can alter the sales compensation packages. Equally, while revenue is initially more difficult to project, a thorough knowledge of how a product is used will give enough information to estimate monthly revenue forecasting.
How Can My Business Calculate Consumption Metrics?
When determining the actual usage of your product, there are four distinct streams that emerge. Each of these fits into a different consumption model, with the knowledge of usage for each case defining the best monetization structure to opt for.
Typically, there are four points that a business can use to determine the usage and billing of their product:
- Discrete Point of Value – Once a particular action is completed, the client will incur a charge. A great example of this is a financial company that charges a fee for every check deposited. The check is either deposited or it is not, with the fulfillment of this condition being small and repeatable, making it a prime candidate for point of value consumption.
- Physical Resource Consumption – As with the earlier medical example, the consumption of a physical resource is perhaps the most straightforward or direct form of consumption billing.
- Time-Block Charging – Charging across blocks of time is appropriate when value is derived from a product over a more extended period of time. This model is commonly used by cloud service providers, where their inherent value is created by extended use
- Logical Resource Consumption – The closest consumption scheme to traditional licensing is where you have a non-reusable logical consumption. An example of this is moving data from point a to point b, creating value upon completion.
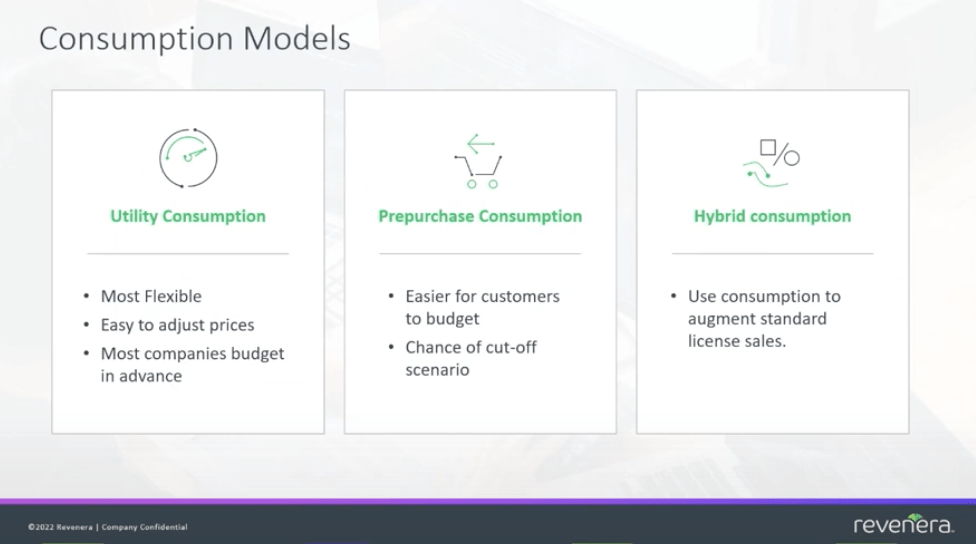
Across these, three further consumption models emerge, selecting aspects of each and combining them. Utility consumption is a flexible model, where a company will bill directly for the amount of resource used up. This is a reflection of physical resource consumption, and, in some cases, logical resource consumption. A generalized example of this is housing utilities; as a person uses up more water or gas, they are billed at a fixed rate.
Yet, this billing scheme evokes the problem of not knowing when to cut off a user. By allowing them to rack up a huge bill, they are using up your resources. If they cannot pay at the end of the billing period, you run into additional costs and losses for your business. The main alternative to this is pre-purchase consumption, where customers buy a fixed amount of a resource.
Once the customer has used all of the resource allocations that they bought, they would then be cut off. This allows customers to budget more effectively, alongside providing an easier method of revenue estimation for the business itself.
Finally, hybrid consumption is where a certain amount of resource is sold to the customer at a flat rate, with any further or additional needs then moving to a utility billing structure. This effectively covers the weaknesses of the first two models, providing maximum flexibility to both customer and business.
Making the Switch To Consumption
Once your company selects an appropriate consumption model, it must then go through the process of actually implementing this software monetization structure. Eric defines three steps to the shift, each building on the next:
- Be sure that your business has all of the required usage data.
- Establish specific rules and documentation for your consumption billing using one of the above models.
- Ensure your company has flexible and powerful entitlement management and licensing solutions to support the change.
Points one and three of this shift can be hard to pin down, with companies needing to have a single point of truth that gives them information about entitlement and usage data within their company.

The third presentation of SoftSummit 2022 discusses the integration of fulfillment and entitlement data to address this challenge.
How Can My Business Manage Entitlements Across On-Premises and SaaS Deployments?
Mark outlined the industry movement towards consumption and Eric detailed why companies are making the switch. Scott’s presentation concluded the subject by explaining how software businesses can structure their usage and billing in order to move to this valuable monetization model. His presentation focused on the integration of entitlement and fulfillment data, with this unification creating a 360-degree view of customer usage and billing across all connected products and channels.
The core metric for success within a consumption model is usage data. Without this, consumption models are unable to effectively manage entitlement, nor bill accordingly for usage. One of the challenges that arises with this is the fact that when businesses perform a SaaS transition and create a cloud version of their app, they often continue to offer their on-premises version, too.

Software businesses need one system that allows them to receive and manage entitlement and usage data in one single location.They may also be driven by customer demand to offer self-service entitlement management that crosses platforms and ensures total flexibility.
Often, businesses will build a middle-layer system between their SaaS and on-site deployment to capture both sets of data. But, with this comes the task of constructing, maintaining, and managing an additional platform. Instead of battling through this tedious task, Scott outlines that integrating entitlement and fulfillment data is the most efficient method.
Dismantling Data Silos Through Integration
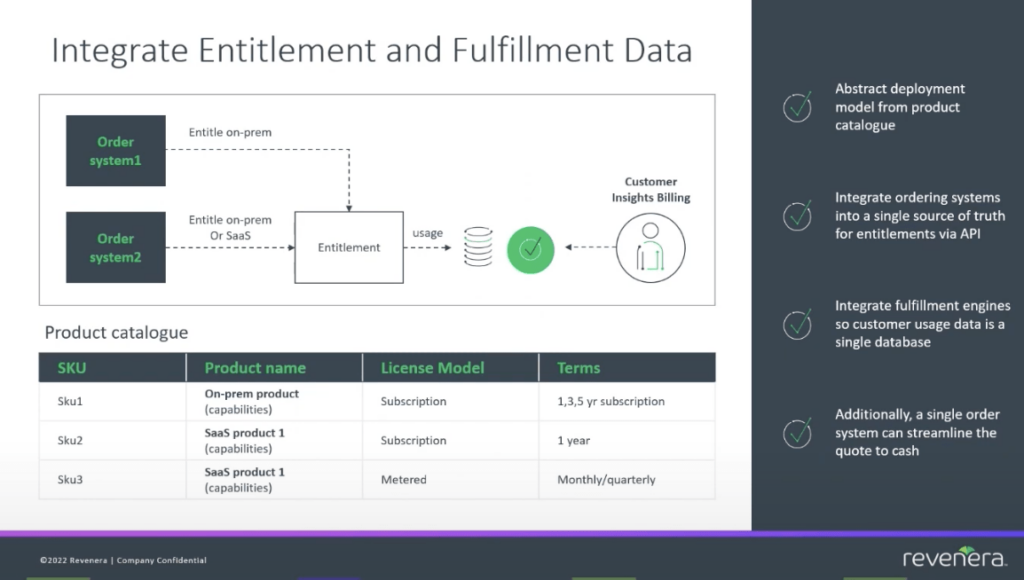
The fastest and most efficient way of creating a single source of truth across different applications (and even across different deployment models) is to integrate both entitlement and fulfillment data. This comes from creating a deployment model from a product catalog, which will directly push entitlement data directly from the order system.
With a central entitlement management system (that supports SaaS and on-premise applications), you have a common interface where a business can understand what someone owns, how that application can be used, and how long they own it for. This flow from order system to entitlement system creates one single layer that has many different systems all speaking into it. From there, you’ll be able to collect usage insights from one platform, no matter how many streams are feeding into it.
Through your order management systems, the entitlement aspect is made into a single source of truth, helping you to get fulfillment records within a single importing database. From the perspective of an end-user, this singular system will describe everything they own, regardless of how it was fulfilled. All the user data, including billing and usage, is in one convenient location.
How Does This Approach To Entitlement and Fulfillment Work?
Within this seamless construction, there are four main steps to work through. This will trace the development pathway from early-stage implementation toward a completely streamlined end process.
Scott outlines the approach as:
- Deploy an Agnostic Product Catalog – Defining what you’re going to market with, what capabilities there are, and what monetization model you’re going to offer is always the first step.
- Convert to a Single Source of Truth for Entitlement Data – Once you establish a common product catalog, you can then integrate this directly into your entitlement system. Regardless of whether you have several order systems or only one, you can integrate all of those APIs into this one entitlement source.
- Integrate Fulfillment Engines – Once customers start to use the products and fulfill the assigned entitlements, you’ll begin to harvest fulfillment data. All the usage data is available to your company in one location due to this further connection.
- Single Order System to Streamline Quote to Cash Process – An additional step that you could take, especially when managing hybrid applications, is streamlining the quote to cash process.
Across these steps, you’ll have created an agnostic product catalog, providing an easy interface for navigation on the customer side of the business. On the back end, the connection to entitlement data and its linked fulfillment data will then provide your company with a complete 360-degree understanding of customer usage and billing.
With this information, your company is perfectly positioned to launch an effective and well-measured consumption software monetization model.
Final Thoughts
Over the course of this segment of the SoftSummit 2022 event, the presentations led by Mark Thomason, Eric Jensen, and Scott Niemann traced the development of software monetization, the company and client benefits of moving to consumption monetization, and concluded with outlining the process and considerations that companies need to follow before making the leap.
From underpinning the causes of the expansion of subscription and consumption software monetization to demonstrating the real processes and information needed to make the conversion, these discussions illuminated an exciting development within the world of software deployment.
Many thanks to all the speakers for sharing their subject expertise. If you want to access the recordings from this event, then be sure to visit the on-demand version of the SoftSummit 2022 software monetization conference for these sessions, plus more from Agilent, Ansys, Infor, BSA, and Product Growth Leaders.




